Bond Work Index
In grinding technologies, the Bond work index is a parameter that measures the amount of energy required for the grinding process of a material. This index is used particularly in the mineral processing and mining sectors.
The bond work index is generally used as follows:
It determines the amount of energy required to grind a material to a certain size. This is used to calculate the energy requirement for the grinding process. The energy requirement varies depending on the grain size and hardness of the material.
Energy requirements guide the selection of suitable grinding equipment.
For example, materials with a high Bond work index value require more energy
and more powerful equipment.
Bond work index is used to evaluate the performance of grinding plants.
This index can help measure how effectively a grinding plant is operating and its energy efficiency.
Usually determined by laboratory tests, and the amount of energy
(kWh/t) required to grind a material to a certain grain size is calculated
as a result of the tests. This value indicates the difficulty of grinding
a particular material.
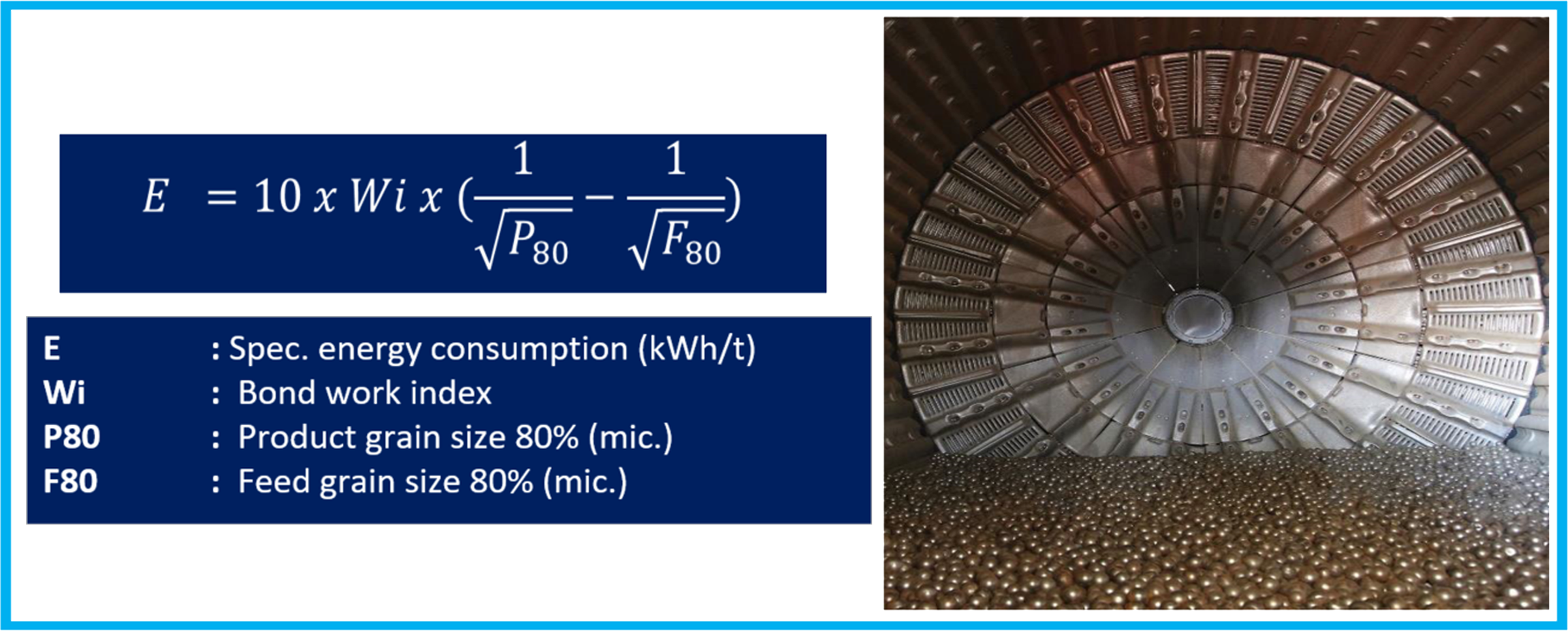
Formula
Material-Index Table
| Material | Bond work Index | Material | Bond work Index | Material | Bond work Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barite | 6,24 | Ferrsilicone | 12,8 | Phosphate Rock | 10,13 |
| Basalt | 20,41 | Flint | 26,1 | Pumice | 11,9 |
| Bauxite | 9,45 | Gabbro | 18,45 | Pyrite Ore | 8,9 |
| Cement Clinker | 13,49 | Garnet | 12,3 | Quartz | 12,7 |
| Chrome Ore | 9,6 | Glass | 3 | Rutile Ore | 12,12 |
| Clay | 7,1 | Granite | 14,37 | Silica Sand | 16,4 |
| Gypsum | 8,16 | Iron Ore | 15,4 | Silicon Carbide | 26,1 |
| Coal | 11,37 | Hematite | 12,6 | Smelter Slag | 15,7 |
| Copper Ore | 13,13 | Magnetite | 10,2 | Blast Furnace Slag | 12,1 |
| Gold Ore | 14,8 | Lead Ore | 11,4 | Sodium Silicate | 13 |
| Dolomite | 11,3 | Lead-Zinc Ore | 11,3 | Syenite | 14,9 |
| Feldspar | 11,6 | Limestone | 11,61 | Titanium Ore | 11,8 |
| Ferrochrome | 8,8 | Calcined Magnesite | 16,8 | Uranium Ore | 17,9 |
| Ferromanganese | 7,7 | Nickel Ore | 11,8 | Zinc Ore | 12,42 |
| * The values given are average values. They may vary depending on the materials. | |||||